In this tutorial you will learn how to interface 16x2 LCD display and similar LCDs with Atmega8 Microcontroller. You will see that how to interface LCD using only 6 IO lines. details about LCD commands and other techniques are explained in 8051 LCD interfacing tutorial present in 89C51 tutorial section.
Objective:
1. To use minimum IO lines to interface LCD.
2. We are using 6-IO Lines
3. To control display on which line it should display
4. Use of minimum components
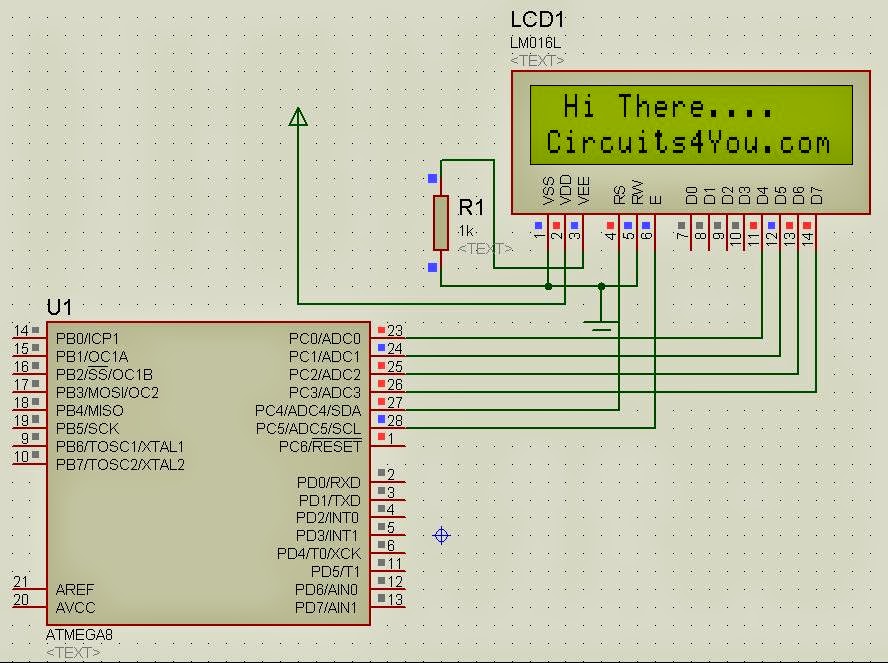
Circuit Diagram :
C Code, Program (AVR Studio 4):
//================================================================= /* 4-Bit mode 16x2 LCD Module Software */ /* 2nd Dec 2005 */ /* Copyright 2005 Circuits4You.com */ /* WWW - http://www.circuits4you.com */ /* Email - info@circuits4you.com */ /* LCD Pin-5(R/W) must be connected to ground*/ //================================================================= #include <avr/io.h> #include <string.h> #define E PC5 #define RS PC4 void display(char string[16], char LineNo); void displaybyte(char D); void dispinit(void); void epulse(void); void delay_ms(unsigned int de); //================================================================= // Main Function //================================================================= int main(void) { DDRC = 0x03F; //Set LCD Port Direction delay_ms(500); //Initiaize LCD dispinit(); delay_ms(200); display(" Hi There....",1); display("Circuits4You.com",2); while(1); } //================================================================= // LCD Display Initialization Function //================================================================= void dispinit(void) { int count; char init[]={0x43,0x03,0x03,0x02,0x28,0x01,0x0C,0x06,0x02,0x02}; PORTC &= ~(1<<RS); // RS=0 for (count = 0; count <= 9; count++) { displaybyte(init[count]); } PORTC |= 1<<RS; //RS=1 } //================================================================= // Enable Pulse Function //================================================================= void epulse(void) { PORTC |= 1<<E; delay_ms(1); //Adjust delay if required PORTC &= ~(1<<E); delay_ms(1); //Adjust delay if required } //================================================================= // Send Single Byte to LCD Display Function //================================================================= void displaybyte(char D) { //data is in Temp Register char K1; K1=D; K1=K1 & 0xF0; K1=K1 >> 4; //Send MSB PORTC &= 0xF0; PORTC |= (K1 & 0x0F); epulse(); K1=D; K1=K1 & 0x0F; //Send LSB PORTC &= 0xF0; PORTC |= K1; epulse(); } //================================================================= // Display Line on LCD at desired location Function //================================================================= void display(char string[16], char LineNo) { int len,count; PORTC &= ~(1<<RS); // RS=0 Command Mode if(LineNo==1) { displaybyte(0x80); //Move Coursor to Line 1 } else { displaybyte(0xC0); //Move Coursor to Line 2 } PORTC |= (1<<RS); // RS=1 Data Mode len = strlen(string); for (count=0;count<len;count++) { displaybyte(string[count]); } } //================================================================= // Delay Function //================================================================= void delay_ms(unsigned int de) { unsigned int rr,rr1; for (rr=0;rr<de;rr++) { for(rr1=0;rr1<30;rr1++) //395 { asm("nop"); } } }
For queries comment...





will you plzz provide the circuit diagram above given is not opening plzz
ReplyDeletevrushalnanavati73@gmail.com is my mail
please can you send the code to my gmail
ReplyDeletespatruni2@gmail.com